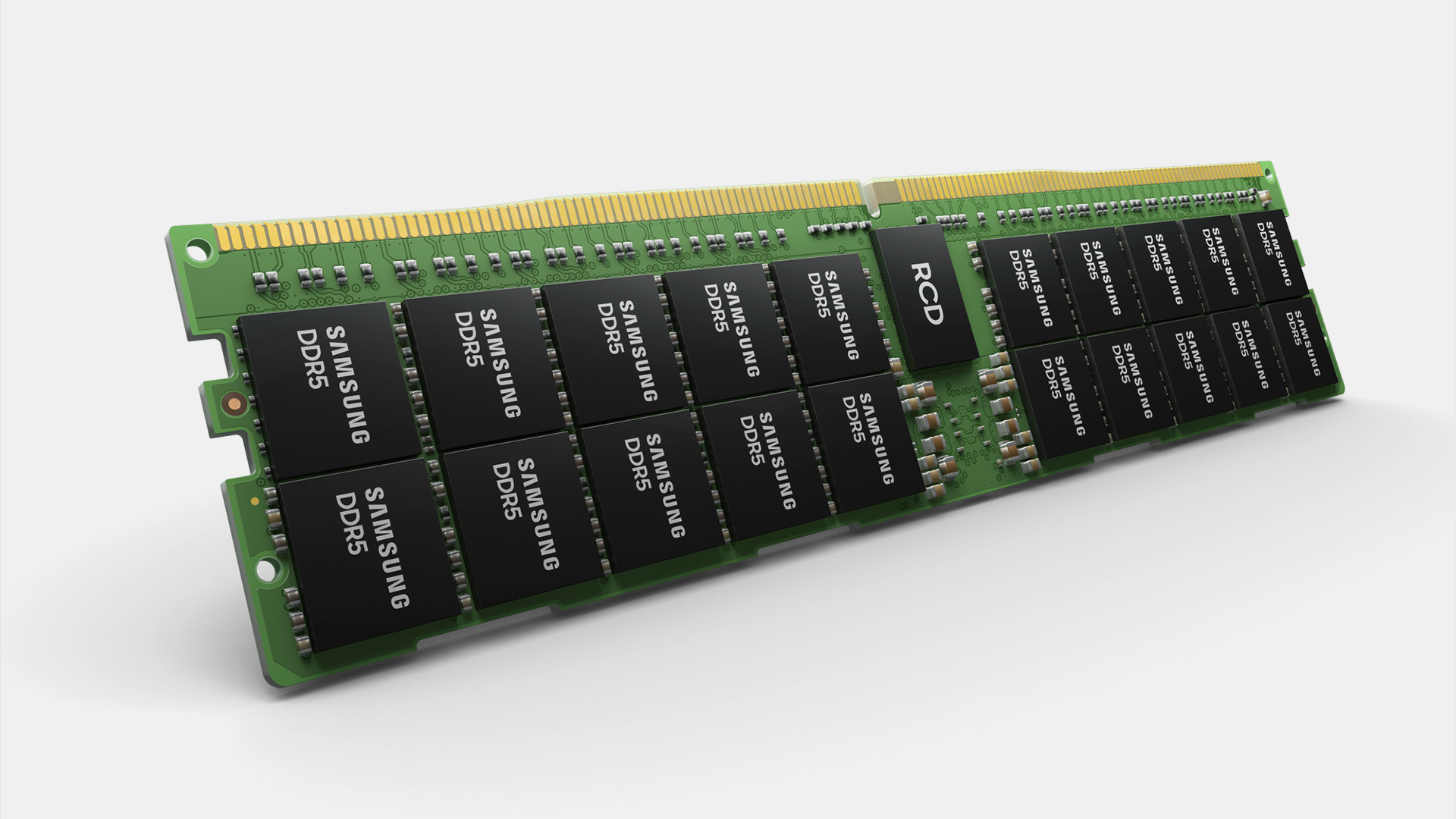
Samsung has announced that it has developed the industry’s first 512GB memory module using its latest DDR5 memory devices that use high-k dielectrics as insulators. The new DIMM is designed for next-generation servers that use DDR5 memory, including those powered by AMD’s Epyc ‘Genoa’ and Intel’s Xeon Scalable ‘Sapphire Rapids’ processors.
Samsung’s 512GB DDR5 registered DIMM (RDIMM) memory module uses 32 16GB stacks based on eight 16Gb DRAM devices. The 8-Hi stacks use through silicon via interconnects to ensure low power and quality signaling. For some reason, Samsung does not disclose the maximum data transfer rate its RDIMM supports, which is not something completely unexpected as the company cannot disclose specifications of next-generation server platforms.
An interesting thing about Samsung’s 512GB RDIMM is that it uses the company’s latest 16 Gb DDR5 memory devices which replace traditional insulators with a high-k material originally used for logic gates to lower leakage current. This is not the first time Samsung has used HKMG technology for memory as, back in 2018, it started using it for high-speed GDDR6 devices. Theoretically, usage of HKMG could help Samsung’s DDR5 devices to hit higher data transfer rates too.
Samsung says that because of DDR5’s reduced voltages, the HKMG insulating layer and other enhancements, its DDR5 devices consume 13% less power than predecessors, which will be particularly important for the 512GB RDIMM aimed at servers.
When used with server processors featuring eight memory channels and two DIMMs per channel, Samsung’s new 512GB memory modules allow you to equip each CPU with up to 8TB of DDR5 memory, up from 4TB today.
Samsung says it has already started sampling various DDR5 modules with various partners from the server community. The company expects its next-generation DIMMs to be validated and certified by the time servers using DDR5 memory hit the market.
“Intel’s engineering teams closely partner with memory leaders like Samsung to deliver fast, power-efficient DDR5 memory that is performance-optimized and compatible with our upcoming Intel Xeon Scalable processors, code-named Sapphire Rapids,” said Carolyn Duran, Vice President and GM of Memory and IO Technology at Intel.