If you buy something from a Verge link, Vox Media may earn a commission. See our ethics statement.
Battery life has been the Achilles’ heel of smartwatches and fitness watches. While solid state storage and processing power have been evolving at a rapid clip, battery life has remained stagnant. This goes quintuple for watches that track your activity using GPS, which is a particularly power-hungry thing to do. And yet, somehow, the Garmin Enduro now exists. If you’re the type of person who likes to run until their kneecaps have been ground into a fine powder, this is the watch for you.
The $800 Enduro is a multisport fitness watch. And by multi, I mean pretty much all the sports. Built-in activities include: Run, Ultra Run, Trail Run, Treadmill, Virtual Run, Track Run, Indoor Track Run, Bike, Mountain Bike, Indoor Bike, Pool Swim, Open Water Swim, Triathlon, SwimRun, Hike, Expedition, Climb, Indoor Climb, Bouldering, Ski, Snowboard, Cross Country Ski, Cross Country Skate Ski, Backcountry Ski, Surf, SUP, Kayak, Row, Indoor Row, Navigate, Track Me, Pilates, Yoga, Breathwork, Cardio, Strength, Golf, and others (including downloadable options made by third parties) but honestly I’m tired of typing. Basically, it has all of the same activity modes as Garmin’s current multisport flagship, the Fenix 6 (starting at $550, up to $1,100), but there are some significant tradeoffs, which I’ll get to in a sec.
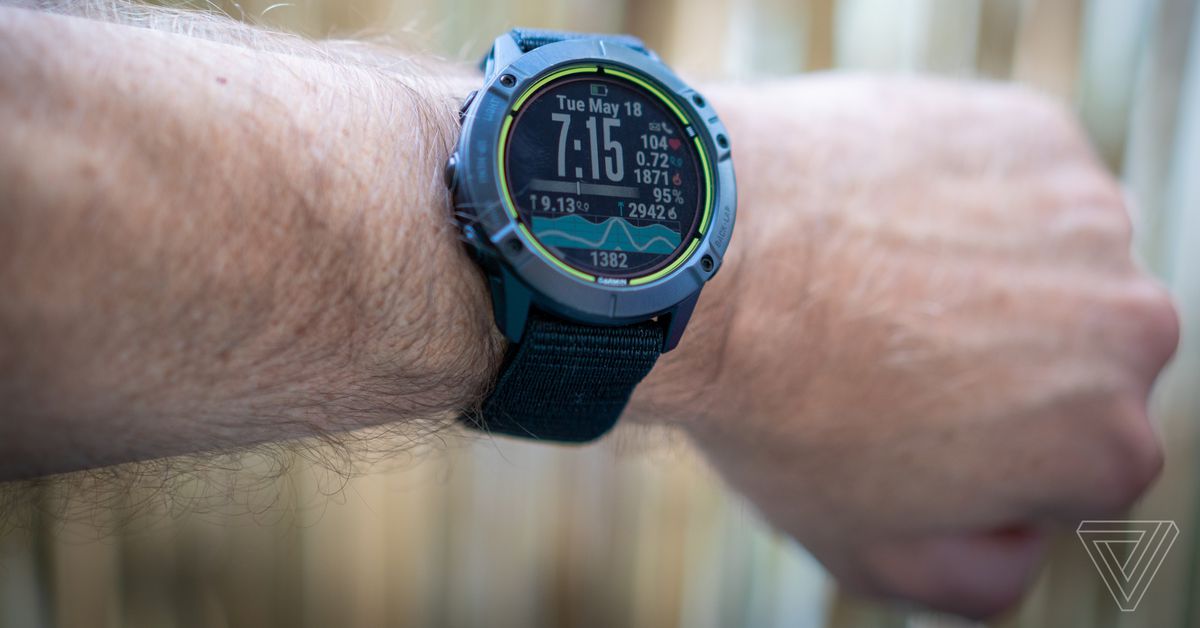
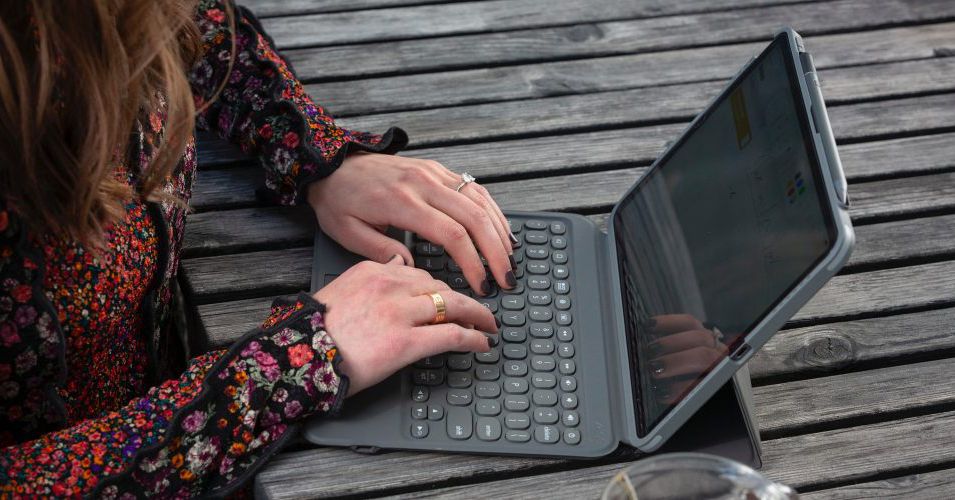
Let’s start with the body. Physically, the Enduro is a perfect twin of the larger Fenix 6X. (You can see a more in-depth comparison between the two on Garmin’s site.) It has a 1.4-inch transflective (sunlight visible) color LCD screen. It’s extremely easy to read, particularly outdoors (at night it lights up with the push of a button). The screen also doubles as a low-key solar panel, giving you extra juice when you wear it outside.
The body is just over two inches by two inches and 0.6 inches thick. In other words, it’s a bit chunky, and people with smaller wrists probably will not like it. I have weirdly big wrist bones, so I didn’t mind the way it felt, and it didn’t look like I was wearing a tablet on my arm. Despite its size it’s quite light, coming in at 71 grams for the steel version or 61 grams for the more expensive titanium version. That weight is partly due to the new, slightly stretchy nylon strap, which is comfortable and dries quickly. There are a lot of other strap options to choose from, should you so desire.
Like the Fenix and most other Garmin watches, the Enduro has five physical buttons which you use for navigating in lieu of a touchscreen. This is the most intuitive of any of the fitness watches I’ve used, and the UI has only gotten better with age.
In addition to being a training watch, it has basic smartwatch features, including displaying notifications from your phone. Android users (like me, I tested it with a Pixel 5) can quick reply to messages from the watch (unfortunately Apple has blocked this feature on the iPhone for any device except the Apple Watch, which seems pretty anti-competitive if you ask me).
From the main screen, pressing the bottom left button (the down button) gets you to a bunch of widgets that provide a lot of data at a glance. It’s just the right amount of information density. If you want more granular info, you can dive into the Garmin Connect app (iOS and Android), which has a lot of detail, but its design is very dated and it can be tricky to find what you’re looking for in it. It’s not bad, but it could benefit from a refresh.
In addition to daily tracking of things like steps, floors climbed, heart rate, sleep quality, and even respiration rate, the Enduro also has a pulse oximeter which uses a special red LED. In my testing, it was roughly as accurate as the finger-based (medical grade) one I bought toward the beginning of lockdown last year. You can choose to have it track your pulse ox 24/7, but that will take a big bite out of your battery life. You can also choose to just track pulse ox as you sleep, which might be good for someone who suffers from sleep apnea. If you don’t have any underlying health concerns, though, I’d just leave it off and check it on demand whenever you want.
The Enduro is primarily a training watch, and it has all of the excellent tools that the Fenix line has, including Body Battery (which surprisingly mapped quite closely to how well rested or depleted I felt), Stress, VO2 Max over time, as well as Training Status. There are some new features debuting on this watch as well. One of the most useful I found was Trail Run VO2 Max. It takes terrain into account, so if you’re running slower because of rocks, it won’t give you an artificially low V02 Max score. Garmin has also upgraded its ClimbPro features, which take ascend and descend into consideration in both your stats and your pace recommendations. The watch can even alert you before you get to a hill (you have to preload a route into the watch) so you can prepare yourself for a climb. There are also new Ultrarunning specific features which I was unable to test because I prefer other ways of injuring myself. It’s worth noting that these new features are also making their way to the Fenix line.
So, why might you want the Enduro over the Fenix? Capital B Battery life. That is really the one and only reason. The battery lasts more than twice as long as the Fenix, and the Fenix is one of the longest-lasting training watches I’ve tested. If you currently use an Apple Watch, you may weep when you read this, but here are the numbers the company claims:
- Smartwatch mode: up to 50 days / 65 days with solar
- Battery Saver Watch mode: up to 130 days / one year with solar
- GPS: up to 70 hours / 80 hours with solar
- Max Battery GPS mode: up to 200 hours / 300 hours with solar
- Expedition GPS Activity: up to 65 days / 95 days with solar
That is absolutely unparalleled. It’s also conservative in my estimation. I wore this watch for a solid month, constantly using it as a smartwatch (checking notifications, checking my vitals, etc). That included 12 hours and 51 minutes of surfing (GPS tracked), four hours and three minutes of running (GPS tracked), and three hours and 16 minutes of strength training (non-GPS). I did not have to take the watch off to charge it at all. Not one single time. It is easily the longest-lasting training / smartwatch I have ever tested, and by a gigantic margin. Garmin claims that it didn’t do this by stuffing in a larger physical battery but by optimizing the underlying platform. I tried to get more details, but they were understandably tight-lipped about the secret recipe.
So, you may see that and think “well then, obviously this is an easy choice over the Fenix 6, right?” Well, not quite. There are some things the Enduro doesn’t have, and they aren’t insignificant.
The biggest thing the Enduro lacks is maps. The Fenix 6 has topographic maps of the entire US built right into it, and that’s been incredibly useful to me. It’s actually kept me from taking wrong turns while hiking on a number of occasions. You can still track back with the Enduro, bread-crumb style, but it will appear as a disembodied trail without any context or landmarks to help guide you. This also means the Enduro doesn’t have some specific cycling training and other navigational features.
The other big thing the Enduro is missing is music. The Fenix allows you to store songs on it and play them via Bluetooth earbuds, so you can leave your phone at home. The Enduro doesn’t. If you want tunes to go with your workout, you’re going to need to carry a second device. This brings up a somewhat frustrating point.
With those things missing, you might assume that it’s because the Enduro has less storage compared to the Fenix. It doesn’t. In fact, it has double the storage of the Fenix at 64GB vs. 32GB. As far as I can tell, the only reason the Enduro doesn’t have maps and music is because Garmin didn’t want to cannibalize sales of the Fenix 6, which is frustrating. If you compare the Enduro to the Fenix 6 Pro Solar edition (which has the same hidden solar-panel display as the Enduro), both watches are a wince-inducing $800. The Fenix is a bit more svelte and has a very slightly smaller screen, but otherwise they’re the same. You just have to choose, do you want maps and all the features they come with, or do you want double the battery life? Garmin could have easily given you both — and perhaps the Fenix 7 or Enduro 2 will have both, or a firmware update could bring maps and music to the Enduro — but for now it’s an either / or between two fantastic features.
It’s a strange dilemma. Ultimately, I think the Fenix 6 is the better, more complete watch, and so that’s the one I would lean toward recommending. You just have to remember to charge it three times as often. That being said, the Enduro is still an excellent watch, and being able to go on a very long trip and leave the (proprietary) charger at home is a real boon, and if you do any ultra-length activities, then this is absolutely the watch you want. For now, I’ll stick with the Fenix 6 in case I get lost, again.
Photography by Brent Rose for The Verge